Complete Guide to Automotive Headlight Socket Types: H1, H3, H4, H7, H11, HB3, HB4 Explained
Understanding headlight socket types is essential for vehicle maintenance, safety, and proper lighting upgrades. Whether you're replacing a burnt-out bulb or planning to upgrade your vehicle's lighting system, knowing the differences between H1, H3, H4, H7, H11, HB3, and HB4 sockets can save you time, money, and frustration.
At Detailing Devils, we recognize that proper headlight maintenance and restoration requires comprehensive knowledge of these socket types and their specific applications.

This detailed guide breaks down each socket type, explaining their design, functionality, compatibility, and practical applications so you can make informed decisions about your vehicle's lighting system.
Understanding Automotive Lighting Standards and Socket Classifications
The ECE Regulation Framework for Headlight Standardization
The World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations (ECE Regulations) developed and maintains international standards for automotive light bulbs, including the socket types discussed in this guide. These standardized classifications exist because vehicles from different manufacturers across the globe require universally compatible replacement bulbs, preventing confusion and ensuring affordability in the aftermarket. Without these standards, each vehicle model would require unique bulbs, making replacements expensive and difficult to source. The three main groups established by these regulations classify automotive bulbs based on their intended use and light output characteristics.
Group 1 bulbs—which include H1, H3, H4, H7, H11, HB3, and HB4—are classified as general-purpose automotive lighting bulbs suitable for headlights, fog lights, and other primary lighting applications. Over 98% of vehicles on the market use one of the eight primary headlight socket types included in Group 1, making familiarity with these types essential for any vehicle owner. Group 2 encompasses smaller marker lights, turn signal bulbs, and accent lighting, while Group 3 contains obsolete bulb types no longer used in modern vehicles. The standardization ensures that replacement bulbs are affordable, widely available, and properly engineered for safe vehicle operation.
Comparison of common automotive headlight bulb socket types including H1, H3, H4, H7, H11, HB3, and HB4 shown in blue plastic adapters.
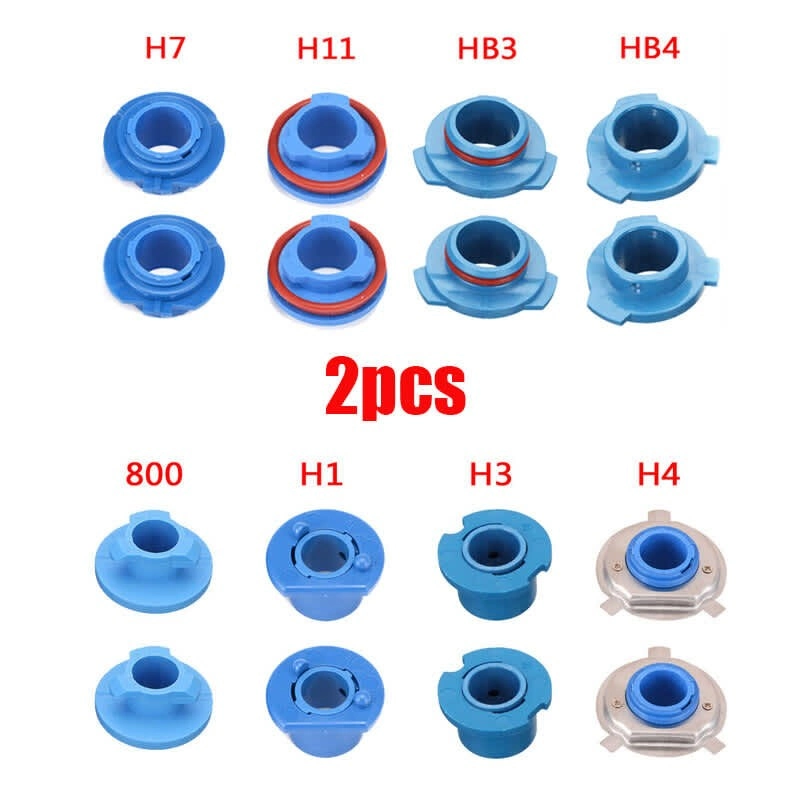

Why Socket Types Cannot Be Interchanged
A critical principle in automotive lighting is that bulb sockets are not interchangeable, even when bulbs have similar specifications. Two bulbs may produce identical light output in watts and brightness, but if one is H1 and the other is H7, the H7 bulb will not physically fit into an H1 socket. This incompatibility exists because each socket type has a unique design, connector configuration, and electrical architecture optimized for specific vehicle headlight housings. Attempting to force an incorrect bulb type into a socket can cause permanent damage, create safety hazards through improper beam patterns, and potentially cause electrical problems including melted connectors or circuit failure.
The socket type used in your vehicle depends on several factors, including the vehicle's manufacturing region, model year, headlight housing design (projector versus reflector), and whether the vehicle uses single-beam or dual-beam configurations. Vehicles from European manufacturers typically use H-series sockets like H7 or H11, while Japanese and American manufacturers often prefer HB-series sockets like HB3 and HB4. Checking your vehicle's owner manual or using online fitment charts remains the most reliable method for identifying your specific socket requirements.
Individual Socket Type Specifications and Applications
H1 Socket: Compact Single-Filament High-Power Option
The H1 socket represents one of the earliest and still widely-used headlight socket types, particularly valued for its compact design and strong, focused beam output. H1 bulbs are single-filament, meaning they produce light through one heating element and provide either high beam or low beam lighting, not both. The socket features a slim, compact shape with a P14.5s base design and a single prong terminal for electrical connection. This straightforward one-terminal design simplifies installation and maintenance, making H1 sockets accessible even for drivers with limited mechanical experience.
Common Applications:
- High beam headlights in single-beam systems
- Low beam headlights where vehicles use separate high and low beam bulbs
- Fog lights in certain vehicle models
- Off-road auxiliary lighting and driving lights
H1 bulbs typically operate at 55-60 watts in 12-volt systems, producing a bright and concentrated beam pattern ideal for highway driving and high-visibility conditions. The compact size facilitates installation in tight headlight housings, and H1 sockets are particularly common in European vehicles, Korean cars, German imports, and American vehicles manufactured from the 1980s through early 2000s. However, modern vehicles have largely shifted toward other socket types, making H1 less common in new car production, though replacement H1 bulbs remain widely available for maintenance purposes.
H3 Socket: Specialized Fog Light Standard
The H3 socket represents a specialized socket type designed primarily for fog lights and auxiliary driving lights rather than primary headlight beams. H3 bulbs feature a single filament and are much smaller and more compact than H1 or H7 bulbs. The H3 socket employs a PK22s base design and uses a wire lead connection rather than standard prong terminals, providing a secure mechanical connection suitable for fog light housings. This wire-lead design differentiates H3 sockets from most other headlight socket types and makes them distinctive during identification.
Common Applications:
- Fog lights and fog lamps
- Driving lights in low-visibility conditions
- Off-road auxiliary illumination
- Accent lighting in certain premium vehicles
H3 bulbs typically produce 55 watts in 12-volt systems and provide strong, focused light output ideal for cutting through fog, mist, and rain. The direct wire connection ensures reliable power transfer, and the compact size accommodates smaller fog light housings common in modern vehicle designs. While not used for primary headlighting, H3 sockets remain important components in comprehensive vehicle lighting systems, particularly in markets where dedicated fog lights are standard equipment. It's crucial not to confuse H3 with HB3—these are completely different socket types with different applications, and H3 bulbs cannot be installed in HB3 sockets.
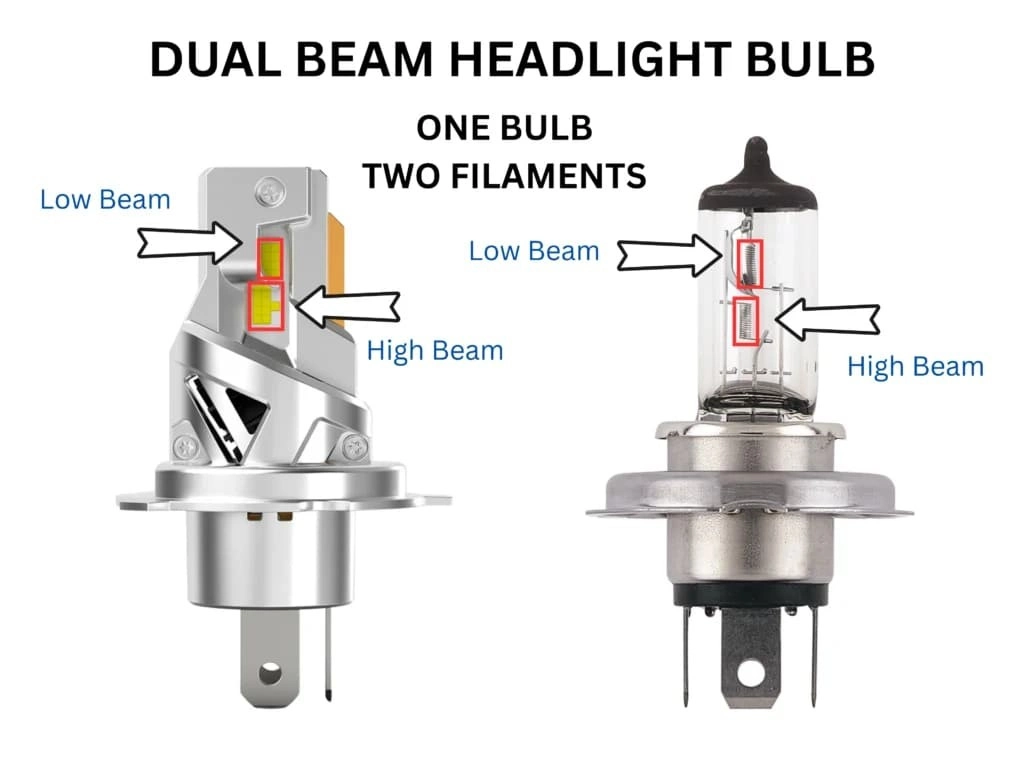
H4 Socket: Dual-Filament Combined Beam Solution
The H4 socket represents a fundamentally different approach to headlight design, accommodating dual-filament bulbs that provide both high beam and low beam functions from a single bulb. This innovative design eliminates the need for separate high and low beam bulbs, simplifying the headlight assembly and reducing the number of components required. The H4 socket employs a round base with a P43t type connector and features three prongs for ground, low beam power, and high beam power connections. This three-prong design distinguishes H4 sockets from single-filament socket types and enables the dual-functionality that makes H4 popular in many vehicle designs.
Common Applications:
- Combined high and low beam headlights in single-pod systems
- Vehicles using non-projector/reflector-type headlight housings
- Budget-conscious vehicle designs minimizing component count
- Aftermarket headlight upgrades for vehicles with compatible housings
H4 bulbs typically operate at 60/55 watts (60 watts for high beam, 55 watts for low beam) in 12-volt systems, providing reliable performance for varied driving conditions. The reliable three-prong design ensures steady power delivery to both filaments, and H4 bulbs are widely available and relatively inexpensive compared to other socket types. H4 sockets remain popular in Japanese vehicles, older American vehicles, and budget vehicle models, though modern vehicles increasingly adopt single-filament designs like H7 that provide superior beam pattern control through twin-pod headlight assemblies. For Detailing Devils customers with older vehicles, H4 headlight maintenance remains a common service involving restoration and protective coating application to maintain optimal light output.
H7 Socket: Modern European Standard Single-Filament Design
The H7 socket represents one of the most widely used headlight socket types in modern vehicles, particularly in European, Asian, and newer generation vehicles globally. H7 bulbs feature a single filament configuration, making them ideal for vehicles using separate pods for high beam and low beam lighting. The socket employs a PX26d base with two prongs for power and ground connections, creating a straightforward electrical architecture suitable for high-power headlight applications. The compact design of H7 sockets facilitates installation in various headlight housings, from projector to reflector types, contributing to their widespread adoption across diverse vehicle platforms.
Common Applications:
- Low beam headlights in European vehicles
- Primary headlight bulbs in most modern sedans and SUVs
- High beam headlights in some vehicle configurations
- Fog lights in certain European vehicle models
H7 bulbs typically operate at 55 watts in 12-volt systems, producing bright, consistent light suitable for both city driving and highway conditions. The H7 socket's popularity stems from its reliability, universal availability, compatibility with both halogen and LED/HID upgrades, and excellent light performance in projector-type headlight housings where precise beam control is critical. For vehicles using projector headlights (common in modern designs), separate H7 bulbs for high and low beams provide superior beam pattern definition compared to dual-filament alternatives. This widespread adoption means H7 replacement bulbs are competitively priced and available at virtually every automotive parts retailer, making maintenance affordable and convenient.
H11 Socket: Popular Modern Low Beam and Fog Light Standard
The H11 socket represents a modern design specifically optimized for single-filament low beam and fog light applications in contemporary vehicles. H11 bulbs feature a wide, flat base (sometimes called a 9006-style connector) with two prongs for power and ground connections, creating a compact, reliable interface. The H11 socket appears frequently in vehicles manufactured in the 2010s and later, reflecting its adoption as a standard for modern lighting systems. Unlike H7, which can be used for both high and low beams, H11 specializes in low beam applications, offering optimized filament positioning for enhanced low-beam pattern accuracy.
Common Applications:
- Low beam headlights in modern sedans and SUVs
- Fog lights in contemporary vehicles
- Daytime running lights (DRLs) that provide automated low-intensity illumination
- Auxiliary lighting in premium vehicle models
H11 bulbs typically operate at 55 watts in 12-volt systems and offer consistent, bright light suitable for both urban and highway driving. The H11 socket's popularity in modern vehicles reflects excellent compatibility with both traditional halogen bulbs and upgraded LED or HID options, providing flexibility for drivers interested in lighting enhancements. H11 sockets appear in Toyota, Honda, Subaru, and other Japanese manufacturers' vehicles, as well as some European models. The widespread adoption means compatible bulbs are widely available, affordably priced, and supported by numerous manufacturers offering quality replacement options. For Detailing Devils customers with modern vehicles, H11 headlight restoration represents a common and straightforward service that dramatically improves nighttime visibility and vehicle appearance.
HB3 (9005) Socket: High-Intensity High Beam Standard
The HB3 socket, also designated as 9005, represents a specialized socket type optimized for high-intensity single-filament high beam applications. HB3 bulbs are specifically designed for powerful, long-range high beam illumination used during highway driving and low-light conditions where maximum visibility is critical. The HB3 socket employs a 9005 base type with a 3-prong connector, featuring a larger profile compared to some competing socket types to safely accommodate the higher-power electrical output characteristic of high beam bulbs. This robust design ensures secure and stable connections that maintain consistent performance even under demanding driving conditions.
Common Applications:
- High beam headlights in modern trucks, SUVs, and performance vehicles
- Auxiliary and accent lighting in some vehicle models
- Performance vehicle lighting systems requiring maximum intensity
- Aftermarket high-output headlight upgrades
HB3 bulbs typically operate at 65 watts in 12-volt systems, producing significantly higher light output than low-beam alternatives. The high-intensity output delivers a bright, concentrated beam ideal for highway driving and dark conditions where maximum visibility prevents accidents and improves driver confidence. HB3 sockets are particularly common in Japanese vehicles, newer trucks, SUVs, and performance cars, with several models using HB3 for both high and low beam functions. The socket's compatibility with both halogen and HID bulbs provides versatility for drivers interested in lighting upgrades, though careful attention to heat dissipation is necessary given the higher electrical demands. It's essential to distinguish HB3 from H3—these are completely different socket types designed for entirely different applications, and confusion between them can result in purchasing incorrect bulbs.
HB4 (9006) Socket: Efficient Low Beam Modern Alternative
The HB4 socket, also designated as 9006, represents a modern socket type optimized for single-filament low beam applications in contemporary vehicles. HB4 bulbs deliver excellent light focus and clarity specifically engineered for low beam requirements, often used alongside HB3 sockets in vehicles employing a dual-socket high/low beam configuration. The HB4 socket employs a 9006 base type with a 2-prong connector, featuring a slightly smaller profile than the HB3 socket while maintaining robust electrical performance. This streamlined design facilitates installation in various headlight housings while providing reliable, consistent electrical connectivity.
Common Applications:
- Low beam headlights in modern sedans, SUVs, and trucks
- Fog lights in certain vehicle models
- Dual-beam systems paired with HB3 high beams
- Common in Japanese and American vehicle manufacturers
HB4 bulbs typically operate at 55 watts in 12-volt systems, producing reliable, consistent light output optimized for low beam applications. The HB4 socket's compact size, reliable design, and excellent light performance have made it an increasingly popular choice for modern vehicle manufacturers. HB4 sockets appear frequently in Honda, Toyota, Nissan, Mazda, and other Japanese manufacturer vehicles, as well as some American domestic vehicles and certain European models. The widespread adoption means HB4 replacement bulbs are readily available from numerous manufacturers at competitive prices, supporting affordability and convenience for vehicle owners. For vehicles using HB3/HB4 combinations, both sockets work in tandem to provide comprehensive high and low beam coverage, offering superior lighting performance compared to single-filament alternatives.

Comparative Analysis: Key Differences Between Socket Types
Filament Configuration: Single versus Dual Systems
The fundamental distinction between headlight socket types centers on filament configuration—whether the bulb contains one or two heating elements. Single-filament socket types (H1, H3, H7, H11, HB3, HB4) produce light through one filament and provide either high beam or low beam lighting. Vehicles using single-filament bulbs require separate bulbs for high and low beams, necessitating two sockets and more complex wiring but offering superior beam pattern control and optical precision. Dual-filament sockets, represented by H4, contain two filaments—one dedicated to high beam and one to low beam—allowing a single bulb to serve both functions.
The choice between single and dual filament designs reflects engineering priorities. Dual-filament H4 systems simplify headlight assembly by reducing component count and cost, making them popular in budget vehicle segments. However, single-filament systems like H7 and H11 in projector headlight housings provide superior beam pattern definition, more precise light distribution, and better optical performance, making them the standard in modern vehicles prioritizing safety and performance. Single-filament designs also facilitate easier LED and HID upgrades, as each beam function can be independently upgraded without compatibility complications.
Base Type and Connector Prong Configuration
Different socket types employ distinct base designs and prong configurations optimized for their specific electrical and mechanical requirements. H1 sockets use a P14.5s base with a single prong, providing simple electrical connection suitable for lower-power applications. H4 sockets employ a P43t base with three prongs to manage dual-filament power distribution. H7 and H11 utilize PX26d and 9006-style bases respectively, with two prongs for power and ground in single-filament configurations.
HB3 (9005) and HB4 (9006) sockets use specialized 90-degree angled bases (P20d and P22d respectively) that differ significantly from other socket types. These 90-degree connectors were designed to optimize electrical contact and mechanical stability in vehicles using these socket types, particularly in Japanese and American vehicles. The prong configuration differences make it physically impossible to install a socket type incorrectly—an H1 bulb simply will not fit into an H7 socket, preventing installation errors that could damage the vehicle's electrical system.
Power Ratings and Light Output Specifications
Automotive headlight bulbs vary in electrical power consumption (measured in watts) and resulting light output brightness, though variations often remain modest across different socket types. H1 bulbs typically operate at 55-60 watts, H3 at 55 watts, H4 at 60/55 watts (dual filament), H7 at 55 watts, H11 at 55 watts, HB3 at 65 watts, and HB4 at 55 watts. The higher wattage of HB3 reflects its specialization for high-beam applications requiring maximum intensity.
Despite differences in wattage, all these bulbs produce broadly similar brightness levels due to differences in filament design, reflector positioning, and optical engineering. A 55-watt H7 bulb in a projector headlight may produce comparable illumination to a 60-watt H4 bulb in a reflector housing due to differences in light distribution efficiency. Comparing bulb types purely on wattage is misleading—the integrated system of bulb type, socket design, housing type, and reflector/projector configuration determines overall lighting performance.
Vehicle Fitment Guides: Finding Your Specific Socket Type
Using Owner's Manuals and Online Fitment Resources
The most reliable method for determining your vehicle's specific headlight socket type involves consulting your owner's manual, which contains definitive specifications for all lighting components. The manual typically includes diagrams showing bulb locations, types, and wattage specifications for headlights, fog lights, and other exterior lighting. If your manual is unavailable or lost, online fitment charts from automotive parts retailers, bulb manufacturers, and specialized sites like Autobahn Technologies or OSRAM provide searchable databases where you enter your vehicle's year, make, and model to receive accurate socket type recommendations.
These online tools prove particularly valuable when dealing with vehicles where manufacturers revised specifications between model years or when distinctions exist between base and premium trim levels. For example, Hyundai Verna vehicles manufactured between 2010-2011 use H4 sockets, 2012-2013 models shifted to HB3/HB4, while 2017-2019 models returned to H4, and 2023-present Verna models use H7. This variation highlights why consulting model-specific fitment data proves essential—assumptions about vehicle lighting can lead to purchasing incorrect bulbs.
Identifying Bulb Type by Direct Examination
When fitment charts are unavailable, directly examining the existing bulb provides definitive socket identification. The bulb's base typically bears markings indicating its type—H1, H4, H7, H11, HB3, or HB4. Carefully remove the existing bulb (ensuring the vehicle is off and the headlight has cooled), examine the base for printed markings indicating the socket type, and record this information. Comparing your bulb's physical appearance to reference images of different socket types provides additional confirmation.
For extremely corroded, damaged, or illegible bulbs, physical comparison to reference samples remains your best option. H4 bulbs are visually distinctive due to their three-prong design, while H1 is noticeably smaller and more compact than H7 or H11. HB3 and HB4 bulbs feature 90-degree angled connectors that distinguish them from other types. Taking clear photographs of your existing bulb and comparing them to reference images online typically provides positive identification within minutes.
Professional Identification Through Detailing Services
If you're uncertain about your vehicle's socket type or prefer professional assistance, Detailing Devils can identify your headlight specifications during consultation or vehicle inspection. Our comprehensive headlight restoration services begin with precise socket type identification, ensuring proper bulb selection for any required replacements or upgrades. This professional identification proves particularly valuable for older vehicles, vehicles with non-standard configurations, or situations where documentation is unavailable.
Socket Compatibility and Upgrading Considerations
LED and HID Compatibility Challenges
While modern LED and HID bulbs are available for most common socket types (H1, H3, H4, H7, H11, HB3, HB4), compatibility challenges extend beyond simple physical fit. LED bulbs often feature significantly different heat sinks and structural designs compared to traditional halogen bulbs, sometimes extending beyond the socket housing and contacting the headlight lens or internal components. This physical incompatibility can prevent proper installation even when the socket connector matches.
Additionally, many modern vehicles employ CAN bus electrical systems that communicate with the vehicle computer regarding component status. Traditional halogen bulbs draw specific power levels that the computer expects, while LED and HID upgrades often consume different power, triggering error messages or causing the vehicle's check engine light to illuminate. Resolving these compatibility issues typically requires CAN bus adapters or decoder modules that "trick" the vehicle computer into accepting the different power consumption. Professional installation becomes advisable for LED and HID upgrades, particularly in modern vehicles with sophisticated electrical systems.
Projector versus Reflector Housing Compatibility
The type of headlight housing in your vehicle significantly impacts socket type compatibility with LED and HID upgrades. Projector-type headlights feature sophisticated optical systems with lens elements that focus light precisely, making them highly compatible with various bulb types when proper positioning is maintained. Reflector-type headlights use curved mirrors to distribute light, with less sophisticated optical control—these housings are specifically engineered for halogen bulbs and often produce unacceptable glare or poor beam patterns when upgraded to LED or HID without complete housing replacement.
Attempting to install HID bulbs in stock reflector-type headlights frequently results in excessive glare that blinds oncoming drivers, poor road illumination, and potential legal issues in regions with strict aftermarket lighting regulations. The intense HID arc requires precise positioning at the reflector's focal point to function properly—a positioning that reflector designs don't accommodate for bulb types other than halogen. For proper HID upgrades, complete projector housing retrofits prove necessary, involving replacement of the entire headlight assembly with projector-equipped housings specifically engineered for HID operation.
Socket Maintenance and Replacement
Over time, headlight sockets can corrode, melt, or fail due to electrical arcing, moisture intrusion, or heat damage. Corroded sockets prevent proper electrical contact, resulting in dim or non-functional headlights even with new bulbs. Melted sockets occur when excessive electrical current flows through undersized connectors, particularly common in vehicles with non-OEM wiring or modified electrical systems. These conditions require professional socket replacement using quality connectors and proper soldering or crimping techniques.
Professional socket replacement involves cutting the old socket from the wiring harness, stripping and soldering new connectors to the existing wires, and securing connections with heat shrink tubing and self-amalgamating tape for weather protection. This specialized work requires electrical expertise and quality materials—improper repairs can cause repeated failures or create fire hazards. Detailing Devils can coordinate with qualified electrical specialists to address socket issues as part of comprehensive headlight restoration, ensuring your lighting system functions safely and reliably.
Practical Applications for Detailing Devils Customers
Pre-Restoration Headlight Assessment
At Detailing Devils, identifying socket type represents the first step in our professional headlight restoration process. By accurately determining whether your vehicle uses H1, H3, H4, H7, H11, HB3, or HB4 sockets, we ensure proper bulb selection for any necessary replacements during restoration. Our technicians assess socket condition, checking for corrosion, arcing, or damage that might compromise headlight performance. If sockets require replacement, we source quality components and perform professional repairs, addressing electrical issues that dim or non-functional headlights often indicate.
Protective Coating Application by Socket Type
Different socket types sometimes benefit from slightly different protective coating approaches based on their specific electrical characteristics and housing design. For instance, HB3 high-beam sockets, operating at higher wattage, generate more heat than H11 low-beam sockets—consideration of thermal characteristics influences coating selection and curing protocols. Detailing Devils applies UV protective ceramic coatings optimized for each socket type's specific operational profile, ensuring maximum protection and durability.
Documentation and Future Maintenance Planning
We provide detailed documentation of your vehicle's socket types during service, enabling smooth future maintenance and ensuring you order correct replacement bulbs. This documentation proves particularly valuable when your vehicle is due for headlight replacements, DIY bulb changes, or upgrades. Understanding your socket specifications prevents purchasing incorrect bulbs, wasting money on incompatible products, and creating frustration during installation attempts.
Conclusion
Understanding automotive headlight socket types—H1, H3, H4, H7, H11, HB3, and HB4—empowers vehicle owners to make informed decisions about maintenance, repairs, and upgrades. Each socket type serves specific applications optimized through decades of automotive engineering evolution, with distinctions in filament configuration, electrical requirements, and beam characteristics reflecting their specialized purposes. Knowing your vehicle's specific socket type prevents purchasing incorrect bulbs, enables smooth maintenance, and ensures compatibility with potential lighting upgrades.
At Detailing Devils, comprehensive headlight care begins with precise socket identification and assessment. Our professional headlight restoration services address not only visibility and appearance through cleaning, restoration, and protective coating, but also electrical integrity through socket inspection and professional replacement when needed. Whether you're maintaining original equipment, planning an upgrade, or addressing lighting issues, understanding headlight socket types represents the foundation of informed vehicle care.
For professional headlight restoration, socket replacement, or lighting system consultation, contact Detailing Devils today. Our expert technicians combine socket type expertise with professional restoration techniques to ensure your vehicle's lighting system performs optimally while achieving the brilliant clarity that makes your car look showroom-new. Don't settle for dim, degraded headlights—invest in professional restoration and experience the safety, visibility, and aesthetic transformation that properly functioning headlights deliver.
FAQ
No, H4 and H7 are physically incompatible and cannot be interchanged. Upgrading from H4 to H7 would require replacing the entire headlight housing and rewiring the electrical connections. This isn't a practical DIY project and should only be considered if your vehicle's mounting points accommodate H7 housings.
HB3 and HB4 are typically used as a pair—HB3 for high beam and HB4 for low beam—in vehicles designed with dual-socket high/low configurations. However, some vehicles use only HB3 for all high beam functions, and others use only HB4 for all low beam functions. Always check your vehicle's specific requirements.
H1 and H3 are completely different socket types with different applications. H1 bulbs are compact single-filament sockets used for headlights, while H3 bulbs feature wire-lead connections and are primarily used for fog lights. H1 bulbs are approximately three times larger than H3 and cannot be physically installed in each other's sockets.
LED bulbs designed for H7 sockets can physically fit and operate in H7 headlight housings. However, compatibility considerations include potential CAN bus errors, beam pattern issues in reflector housings, and heat management. Professional installation and quality LED bulbs specifically designed for your vehicle ensure optimal performance and safety.
Corroded sockets require professional replacement using quality connectors and proper soldering techniques. Attempting to use corroded sockets risks electrical failure, dim headlights, and potential fire hazards. Contact Detailing Devils or a qualified automotive electrician for professional socket replacement and restoration.
Related Blogs:
- Best Car Cleaning Service in Noida - Find the best car cleaning services in Noida and keep your car looking new.
- Car Detailing Products - Discover the best products for car detailing and how to use them to achieve a professional shine.
- Detailing Services for Different Cars - Learn about the different types of detailing services available for different types of cars and which one is best for you.
- Car Detailing for Different Seasons - Find out how to prepare your car for different seasons with the right detailing methods and products.
- How to clean your car's interior - Learn the 8 best techniques and products for cleaning the interior of your car, including the seats, dashboard, and carpets.

